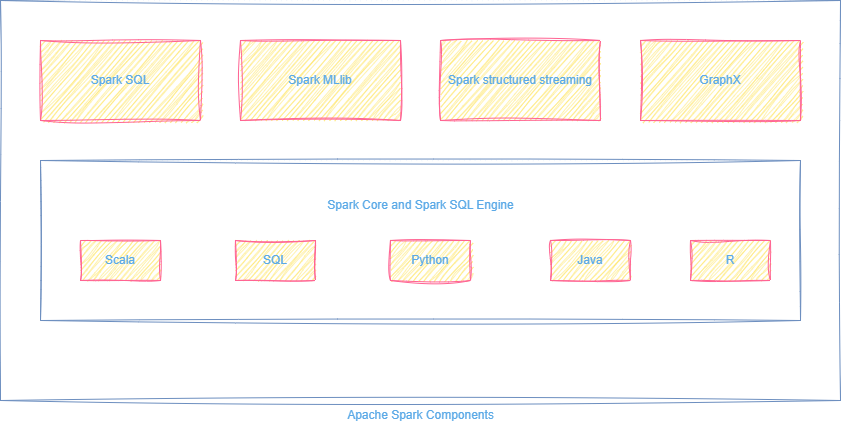
Components of Apache Spark
Apache Spark isn’t just one tool—it’s a modular platform made up of powerful libraries, all running on a single execution engine.
This modular design allows Spark to handle diverse workloads like batch processing, real-time streaming, machine learning, and graph processing.
Let’s explore Spark’s major components:
Key Features:
Use Case:Running ad-hoc queries on large datasets stored in Azure Data Lake or Hive, without a dedicated SQL engine.
Key Features:
Use Case:Predicting customer churn or detecting fraud in real-time financial transactions using behavioral data.
Key Features:
Use Case:Monitoring server logs, clickstream behavior , or IoT sensor streams for real-time alerts and insights.
Key Features:
Use Case:Detecting communities in a social network, or calculating optimal paths in a transportation system.
|
Component |
Purpose |
What It Does |
|---|---|---|
|
Spark Core |
Foundation engine |
Handles distributed task scheduling, memory management, and fault recovery for all workloads |
|
Spark SQL |
Structured data processing |
Query relational data using SQL or DataFrames ; optimizes queries automatically |
|
Spark MLlib |
Machine learning library |
Provides scalable algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, and recommendations |
|
Structured Streaming |
Real-time processing |
Treats live data streams as unbounded tables; enables SQL on streaming data |
|
GraphX |
Graph processing |
Analyzes relationships and networks; includes PageRank and community detection algorithms |
💡 Did You Know?
• Structured Streaming uses Spark SQL’s engine behind the scenes, so you can stream with SQL!
• GraphX can scale to billions of edges, making it ideal for analyzing large-scale networks like Twitter or LinkedIn.
• MLlib moved from RDD-based APIs ( spark.mllib ) to DataFrame -based APIs (spark.ml) for better performance and usability.
📚 Study Notes
Key Features of Spark
• Spark SQL enables SQL querying on distributed data with BI tool integration.
• MLlib simplifies ML workflows using built-in pipelines and scalable algorithms.
• Structured Streaming treats real-time data as an unbounded table for seamless processing.
• GraphX enables parallel graph computation on massive datasets using standard Spark APIs.
