Spark Architecture
Apache Spark is designed to process big data by distributing tasks across multiple machines. Its architecture ensures high speed, scalability, and fault tolerance—making it a top choice for modern data systems.
Spark Follows a Master- Worker Architecture
Apache Spark processes large-scale data across distributed machines using a Master-Slave architecture.
The Driver coordinates the job, and Executors handle the actual execution in parallel across nodes.
At a high level, Spark consists of three key components:
Spark Architecture Overview
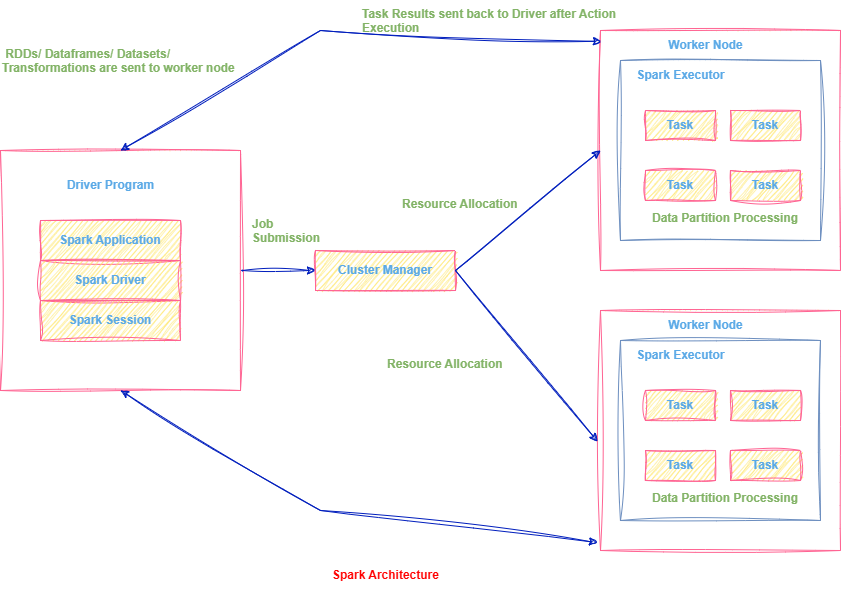
Driver Program: Includes Spark Application, Driver, and Session. Submits the job and controls execution.
Cluster Manager: Allocates resources and launches Executors on Worker Nodes.
Worker Nodes (Executors): Run tasks and process data partitions in parallel.
Task Flow: Data and transformations are sent to Executors; results flow back to Driver after execution.
Step-by-Step: Spark Execution Flow
Let’s walk through what happens behind the scenes when you run a Spark job:
Quick Breakdown of the Flow:
💡 Did You Know?
• Executors are short-lived or long-running depending on your cluster mode—batch jobs vs streaming.
• You can monitor Spark jobs using the Spark UI, which shows DAGs, stages, tasks, memory usage, and more.
• Spark’s Fault Tolerance comes from re-executing failed tasks based on lineage information in RDDs.
📚 Study Notes
Master Worker Architecture
• Driver = Master → Coordinates the Spark job, maintains metadata, and converts code into a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) of stages & tasks.
• Cluster Manager = Resource Dispatcher → Allocates resources (CPU, memory) across the cluster. Can be Standalone, YARN, Mesos, or Kubernetes.
• Executors = Workers → Run on worker nodes; they execute tasks and store data in memory/disk.
• Spark translates user code → DAG → Optimized Physical Plan → stages → tasks → parallel execution.
• Spark supports multiple cluster managers, making it highly portable across environments.
How Spark executes the job –
• User submits a job (Eg – PySpark code).
• Driver converts the job into a DAG (Stages & Tasks).
• Cluster Manager allocates resources (Executors on Worker Nodes).
• Executors process tasks in parallel (Processing Partitions of Data).
• Executors send results back to Driver (Final Output).
